Causes of Premature Motor Failure
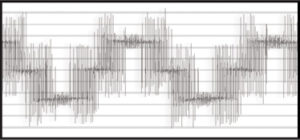
The Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) Drive’s “Voltage Source Inverters” use IGBT’s to switch voltage on and off rapidly to form a PWM voltage source for the motor. This allows the motor to operate as though it were under the influence of a Sine Wave voltage source, except that the drive can change the “fundamental frequency” of the PWM waveform, thus changing the speed at which the motor turns.
The drawback to the PWM scheme is that the rapid switching transitions cause overshoots in voltage due to parasitic capacitance (also related to common mode current) and inductance in the motor’s leads. The parasitic components behave according to the equations I = C * dv/dt and V = L * di/dt. The faster the drive switches (or, as dv/dt rises) the higher the surge currents will be in the leads. This in turn causes high voltage pulses across the parasitic inductances.
In the end, the faster the pulses switch, the greater the impact of cable capacitance and inductance. These fast voltage pulses stress the motor’s windings, causing heat and possibly premature failure. There is also capacitance in the motor’s bearings due to the grease and air preventing direct and continuous contact. Again I = C dv/dt causes current to flow through the bearings, more as the switching speed rises. This can lead to premature bearing failure. As it happens, high switching speed allows the drive to operate with higher efficiency so this is a desirable trait. Motors that are not designed to conform to MG-1 requirements should be protected with sine wave filters or dv/dt filters depending on the specific situation.
May be related to:
- Carrier Suppression
- Switching Speeds
- Carrier Attenuating
Motor Protection Solutions
MotorGuard Sinewave Filter
- Specific Applications can reach 15,000 feet
- Reduce Common Mode Current
- Reduction in Bearing Currents
- Reduction in Instrumentation Reference to Ground Noise
- Reduce Motor Noise, Vibration, and Heat
- Increase in Motor Life
- Elimination of Torque Ripple
- Elimination of Voltage Wave Reflection
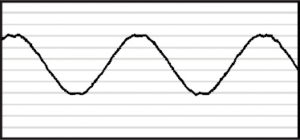
After MotorGuard
The MotorGuard filter converts the PWM wave form to a near sinusoidal wave form, allowing sensitive applications to take advantage of the efficiencies and savings that PWM output power supplies and drives offer.
MotorShield Sinewave Filter
- Specific Applications can reach 15,000 feet
- Elimination of Voltage Wave Reflection
- Resistor-less Filter reduces motor noise, vibration, and heat
- Increase in Motor and Cable life
- Compact, small footprint
After MotorShield
The MotorShield filter reduces the effects of reflected wave phenomenon (dv/dt), which can cause motor heating and insulation damage. The reduction of high frequency VFD output currents extend the life of motors and cables.